geo textile material
1.Exceptional Durability
2.Lightweight & High Strength
3.Superior Filtration & Drainage
4.Cost-Effective & Eco-Friendly
5.Flexibility & Adaptability
1.Introduction Polypropylene (PP) geotextile
Polypropylene (PP) geotextile is a high-performance synthetic geosynthetic material fabricated from polypropylene resin via processes like melt spinning, non-woven needling, or weaving. It features a porous, flexible structure with excellent compatibility with soil, water, and construction materials, serving as a critical auxiliary material in civil engineering, environmental protection, and infrastructure projects.
2. Core Advantages
• Exceptional Durability: Resistant to corrosion, aging, and chemical erosion (e.g., acids, alkalis, salts), maintaining structural integrity in harsh environments without degradation.
• Lightweight & High Strength: Boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, enabling easy transportation, installation, and on-site handling while providing reliable tensile and tear resistance.
• Superior Filtration & Drainage: The porous structure effectively filters soil particles to prevent clogging, while facilitating rapid water permeation to reduce hydrostatic pressure in engineering structures.
• Cost-Effective & Eco-Friendly: Low raw material costs and energy-efficient production reduce overall project expenses; recyclable properties align with sustainable construction standards.
• Flexibility & Adaptability: Conforms well to irregular terrain and structural deformations, ensuring close contact with substrates and enhancing project stability.
3. Key Applications
• Civil Engineering: Roadbed reinforcement (prevents soil subsidence), pavement separation (isolates aggregates and soil), and slope protection (reduces erosion).
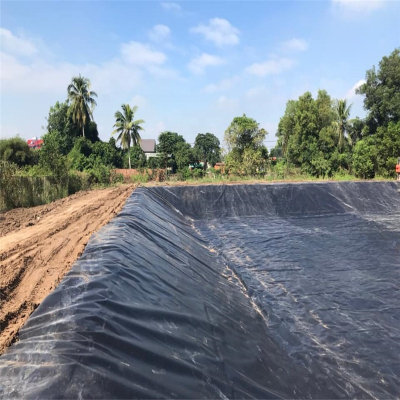
• Water Conservancy & Hydraulic Engineering: Riverbank stabilization, reservoir lining filtration, drainage systems for irrigation canals, and flood control projects.
• Environmental Protection: Landfill liner protection (prevents contaminant leakage), sewage treatment filtration, and ecological restoration (vegetation growth support).
• Construction & Infrastructure: Foundation drainage for buildings, basement waterproofing, and soil stabilization in airports, ports, and railway projects.
4. Production Process Flow
1. Raw Material Preparation: Select high-purity polypropylene resin (with additives like UV stabilizers or antioxidants) and undergo drying to remove moisture (moisture content < 0.5%).
2. Melt Spinning: Feed dried resin into an extruder, melt at 200–230°C, and extrude through spinnerets to form continuous PP filaments.
3. Web Formation: Deposit filaments onto a conveyor belt via air-laying or carding to form a uniform non-woven web (for needled products) or interweave filaments via weaving machines (for woven products).
4. Consolidation: For non-woven geotextiles, use needle-punching machines to entangle fibers mechanically; for woven types, enhance fabric density via calendering.
5. Post-Treatment: Apply heat setting (to improve dimensional stability), UV resistance coating, or anti-static treatment based on application requirements.
6. Slitting & Rolling: Cut the finished fabric into standard widths (2–6m) and roll into coils with specified lengths, followed by quality inspection (tensile strength, permeability, and thickness tests) before packaging and delivery.