hdpe dam liners
• Superior Seepage Control.
• Enhanced Mechanical Strength.
• Dual Protection & Durability.
• Easy Installation & Adaptability.
• Cost-Effective Total Solution.
1. Introduction
Composite geomembrane, a high-performance geosynthetic material, is engineered by laminating one or more layers of impermeable geomembrane (typically HDPE, LDPE, or LLDPE) with non-woven/woven geotextiles
(polypropylene or polyester) via thermal bonding, adhesive lamination, or needle-punching. It integrates the impermeability of geomembranes with the reinforcement, filtration, and protection functions of geotextiles, forming a versatile,
durable barrier system. Compliant with international standards such as ASTM D751, EN 13763, and ISO 10713, it is widely recognized in global civil engineering, environmental protection, and infrastructure projects as a reliable solution
for seepage control and structural enhancement.
2. Core Advantages
• Superior Seepage Control: Boasts ultra-low permeability (≤1×10⁻¹⁰ m/s for HDPE-based composites), effectively preventing water, leachate, or chemical seepage—meeting strict environmental and engineering requirements worldwide.
• Enhanced Mechanical Strength: The geotextile layer reinforces tensile strength, tear resistance, and puncture resistance, enabling the membrane to withstand harsh construction conditions (e.g., uneven substrates, heavy equipment) and long-term operational loads.
• Dual Protection & Durability: The outer geotextile shields the inner geomembrane from abrasion, UV radiation, and chemical corrosion, extending service life to 50+ years in typical applications—reducing long-term maintenance costs.
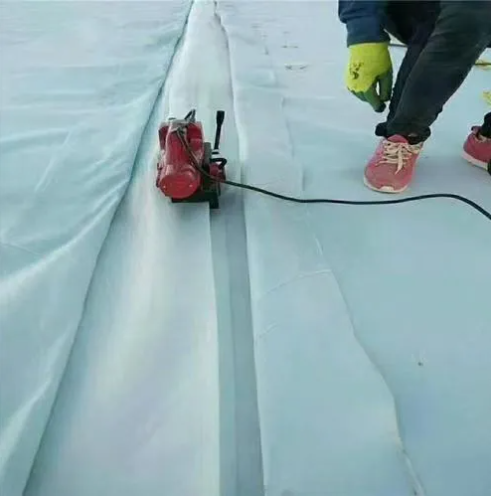
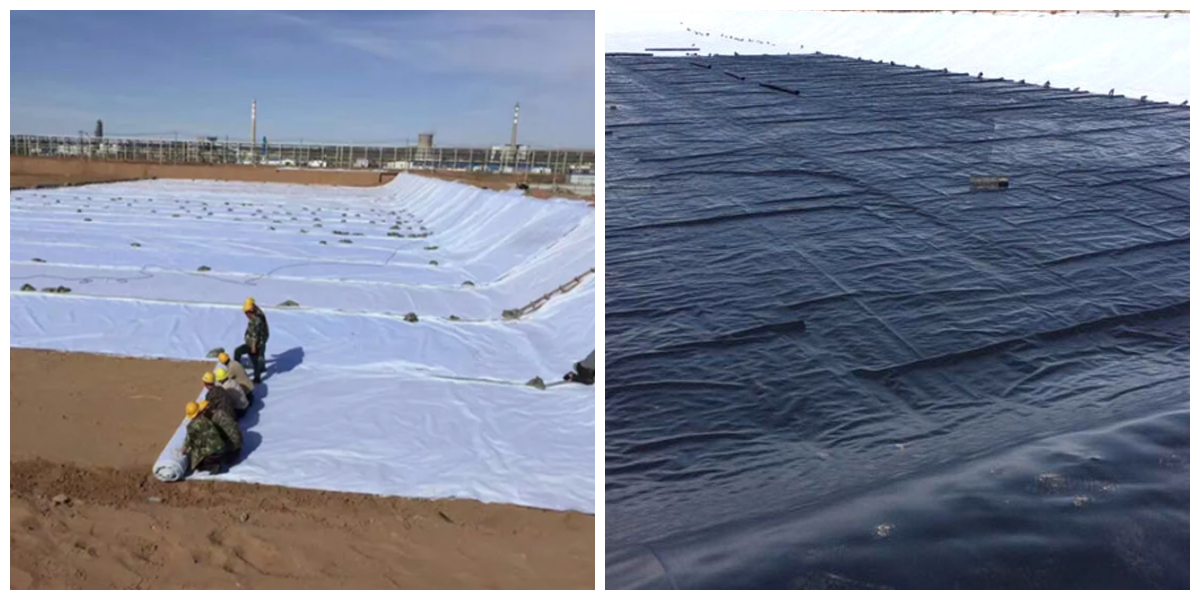
• Easy Installation & Adaptability: Lightweight, flexible, and easy to weld (for thermoplastic membranes) or overlap, it adapts seamlessly to complex project shapes (e.g., irregular reservoirs, sloped embankments) and minimizes installation time/labor.
• Cost-Effective Total Solution: Combines multiple functions (impermeability, reinforcement, filtration) into a single product, eliminating the need for separate materials and lowering overall project costs while ensuring performance reliability.
3. Key Applications
• Environmental Protection: Landfill liners and caps (complying with EU Landfill Directive, US EPA regulations) to contain contaminants; mine tailing pond liners, hazardous waste sites, and brownfield remediation projects.
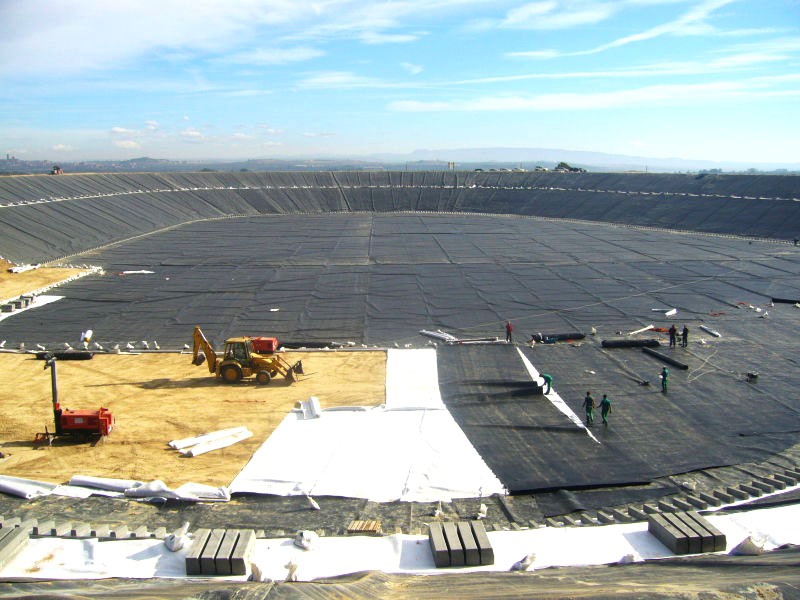
• Water Resources Management: Reservoirs, canals, dams, and water storage ponds (critical for water-scarce regions like the Middle East, Australia); wastewater treatment plants, sewage lagoons, and drinking water tank liners.
• Civil Infrastructure: Highway and railway subgrade waterproofing; tunnel linings, basement and underground structure seepage control; coastal reclamation, dike reinforcement, and flood protection barriers.
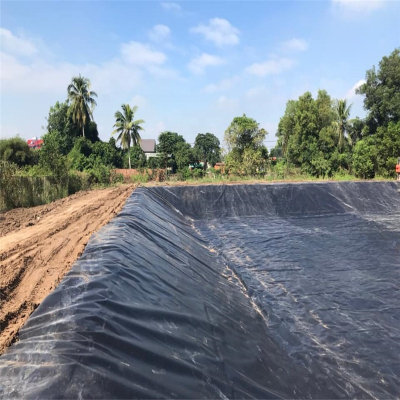
• Agriculture & Aquaculture: Irrigation channel liners (reducing water loss); fish/shrimp pond liners (maintaining water quality and preventing seepage) for global aquaculture industries.
• Energy & Industrial Projects: Oil/gas storage tank bases, chemical pond liners, and renewable energy (e.g., solar farm site waterproofing, biogas digester liners).
4. Manufacturing Process
1. Raw Material Selection & Inspection: High-grade resins (HDPE/LDPE/LLDPE) and geotextiles are sourced from certified global suppliers, with strict testing for purity, tensile strength, and UV resistance to ensure compliance with international standards.
2. Geomembrane Extrusion: Resins are melted, extruded through a flat die, and cooled to form a continuous geomembrane sheet—controlled for uniform thickness (0.3–3.0 mm) via precision calendering.
3. Geotextile Preparation: Non-woven/woven geotextiles are inspected for gram weight, tensile strength, and permeability, then pre-treated (if needed) to enhance bonding with the geomembrane.
4. Lamination & Bonding: The geomembrane and geotextile layers are bonded via thermal lamination (heat pressing for thermoplastic compatibility) or adhesive lamination (eco-friendly, high-strength adhesives for specialized combinations),
ensuring full-surface adhesion without bubbles or delamination.
5. Post-Processing: The composite sheet is trimmed to standard widths (3–8 m) and lengths (50–100 m), then subjected to quality testing (permeability, peel strength, tensile strength) by third-party labs (SGS, Intertek).
6. Packaging & Storage: Finished rolls are wrapped in moisture-proof, UV-resistant packaging with product labels (certifications, specifications, batch numbers) for safe sea freight and on-site storage, ensuring no damage during transportation.